|
| HOME | About us | Technologies | Services | Consulting | Business Development | |
|
|
 |
|---|
| Events
Discovery & Development Europe 2025: Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress 8th European Cyclodextrin Conference |
|
|
Proof of Efficacy
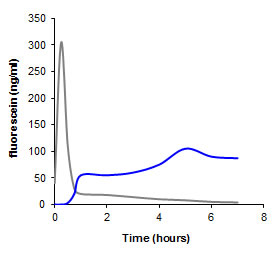
Ocular InsertsThe mucoadhesive properties and the potential to provide a controlled drug release out of thiolated polymers were recently demonstrated in human volunteers. Due to the mucoadhesive properties of the delivery system lasting for at least 8 hours and a controlled release of the model drug sodium fluorescein, a constant level of the test compound could be maintained in the tear fluid/cornea for numerous hours (blue graph). In contrast, using the same polymeric carrier matrix without thiol groups, the effect was gone within an hour (grey graph) [Hornof, M.D., Weyenberg, W., Ludwig, A., and Bernkop–Schnürch, A. (2003). A mucoadhesive ocular insert: Development and in vivo evaluation in humans. J. Control. Rel,. 89, 419].
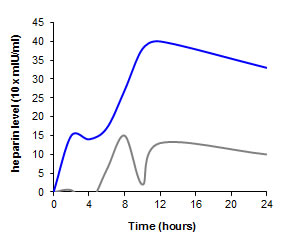
Oral bioavailability of hydrophilic macromolecular drugs Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)The oral bioavailability of LMWH is negligible, as this hydrophilic macro-molecule can only hardly pass the gastrointestinal absorption membrane. Even by the use of well-established drug delivery systems with permeation enhancing properties the uptake of LMWH is poor as recently shown in rats (grey graph). Utilizing the thiomer-technology, however, the plasma LMWH level can be strongly improved (blue graph) reaching an absolute oral bioavailability of at least 20%. For more details please read Kast et al. [Kast, C.E., Guggi, D., Langoth, N. and Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2003) Development and in vivo evaluation of an oral delivery system for low molecular weight heparin based on thiolated polycarbophil. Pharm. Res., 20, 931].
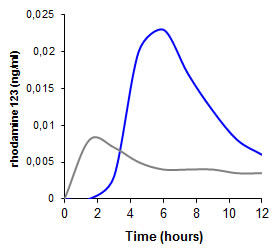
Oral bioavailability of efflux pump substrates Rhodamine 123Rhodamine 123 is a well-known substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Due to the activity of P-gp in the GI-tract its oral bioavailability is comparatively very poor (grey graph). Studies in rats, however, demonstrated that by the co-administration of thiolated polymers its oral uptake can even be more than 1.6-fold improve (blue graph) [Föger F., Schmitz Th., Kafedjiiski K. and Bernkop-Schnürch A. (2006) In vivo evaluation of an oral delivery system for P-gp substrates based on thiolated chitosan, Biomaterials, 27, 4250].
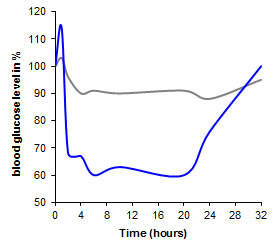
Pharmacological efficacy of orally given peptide drugs InsulinBecause of enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and poor absorption form the intestine orally administered insulin has no effect on the blood glucose level. Accordingly, the effect of orally administered insulin on the glucose level of diabetic mice is also of no significance (grey graph). In contrast, a significant reduction of the glucose level is achieved by incorporating the peptide in a thiolated polymer (blue graph). Utilizing the thiomer-technology a pharmacological efficacy of the oral formulation versus s.c. injection of 7% was reached. For more details please read Caliceti et al. [Calceti P., Salmaso S., Walker G., and Bernkop-Schnürch A. (2004) Development and in vivo evaluation of an oral insulin-PEG delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 22, 315].
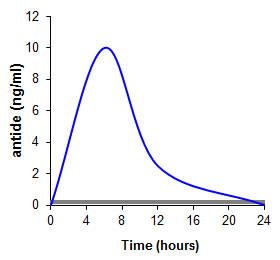
AntideThe therapeutic peptide antide is an antagonist of gonadotropin hormone-releasing hormone, which has been studied for the treatment of prostate and breast cancer, endometriosis and uterine fibrosis. When being orally administered with state-of-the-art delivery systems (grey graph), the peptide drug does not at all reach the systemic circulation. Utilizing the thiomer-technology, however, an absolute and relative (vs subcutaneous) bioavailability of 1% and 3% was achieved in pigs, respectively (blue graph) [Bernkop-Schnürch A., Pinter Y., Guggi D., Kahlbacher H., Schoffmann G., Schuh M., Schmerold I., Del Curto M.D., D'Antonio M., Esposito P., and Huck C. (2005) The use of thiolated polymers as carrier matrix in oral peptide delivery--proof of concept. J. Control. Release., 106, 26]. In another study oral administration of antide in solution led to a bioavailability of 0.03% in rats. In contrast, with antide incorporated in matrix tablets comprising a preactivated thiolated polymer a bioavailability of 10.9% could be reached resulting in a 421-fold increased area under the plasma concentration time curve compared to the antide solution [Dünnhaupt, S., Barthelmes, J., Iqbal, J., Perera, G., Thurner, C.C., Friedl, H. and Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2012) In vivo evaluation of an oral drug delivery system for peptides based on S-protected thiolated chitosan. J. Control. Release., 160, 477].
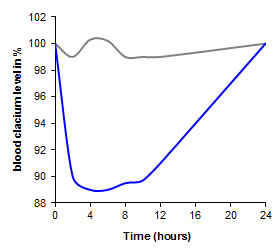
Salmon CalcitoninBiofeedback studies in rats showed, that the calcium level cannot be lowered by the oral administration of salmon calcitonin using well-established delivery systems (grey graph). In contrast, a pharmacological efficacy of 1.3% was achieved in rats by utilizing a thiolated polymer as drug carrier matrix (blue graph). For more details please read Guggi et al. [Guggi D., Krauland A.H., and Bernkop-Schnürch A. (2003) Systemic peptide delivery via the stomach: in vivo evaluation of an oral dosage form for salmon calcitonin. J. Control. Release, 92, 125].
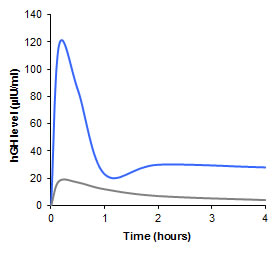
Bioavailability of nasally administered peptide drugs Human Growth Hormon (hGH)Because of its comparatively high molecular mass being in the range of 22 kDa, hGH is not absorbed from the nasal cavity in significant quantities (grey graph). Utilizing a thiomer as auxiliary agent, however, an absolute nasal bioavailability of 2.6% was reached (blue graph). More recent studies showed that by making use of another thiomer formulation an even higher nasal bioavailability for hGH in the range of 8% can be gained [Leitner V.M., Guggi D. and Bernkop-Schnürch A. (2004) Thiomers in noninvasive polypeptide delivery: in vitro and in vivo characterization of a polycarbophil-cysteine /glutathione gel formulation for human growth hormone. J. Pharm. Sci,. 93, 1682; Leitner V.M., Guggi D., Krauland A.H. and Bernkop-Schnürch A. (2004) Nasal delivery of human growth hormone: in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a thiomer/glutathione microparti-culate delivery system. J. Control. Release., 100, 87].
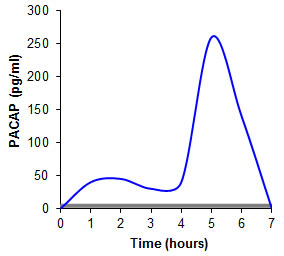
Bioavailability of buccally administered peptide drugs Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide (PACAP) PACAP is a therapeutic peptide useful for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Utilizing unmodified chitosan or other state-of-the-art auxiliary agents the peptide is not at all uptaken from the buccal mucosa (grey graph). In contrast, when being incorporated in thiolated chitosan and applied in form of buccal patches an absolute bioavailability of at least 1% was achieved in pigs (blue graph) [Langoth, N., Kahlbacher, H., Schöffmann, G., Schmerold, I., Schuh, M., Franz, S., Kurka, P. and Bernkop-Schnürch, a. (2006) Thiolated chitosans: design and in vivo evaluation of a mucoadhesive buccal peptide drug delivery system, Pharm. Res., 23, 573]. |
News
Thiomatrix joined the EU-project TENTACLE (101191747) focusing on the use of thiomers for in situ bioprinting.
|
|
|---|
© All rights reserved | Site map | Disclaimer | Imprint | Contact | |
|
||
| TM |