|
| Events
Discovery & Development Europe 2025: Formulation & Drug Delivery Congress
July 1-2, 2025
Basel, Switzerland
Invited lecture:
Oral Delivery Of Peptide And Protein Drugs – Oral Delivery of GLP-1 Analogues
Prof. Dr. A. Bernkop-Schnürch
more...
8th European Cyclodextrin Conference
September 9-12, 2025
Milano, Italy
Invited lecture:
Thiolated Cyclodextrins in Drug Delivery
Prof. Dr. A. Bernkop-Schnürch
more...
|
|
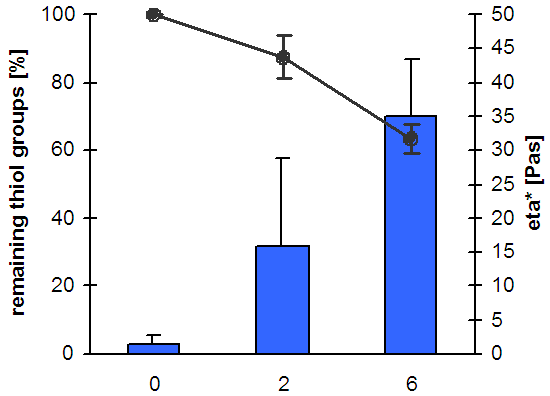
Correlation between the
decrease in thiol groups (graph) because of the formation of disulfide bonds
and the increase in viscosity (bars) of thiolated chitosan [Hornof, M.D., Kast, C.E., and Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2003). In vitro evaluation of the viscoelastic properties of chitosan - thioglycolic acid conjugates. Eur J. Pharm. Biopharm., 55, 185].
|
|
In Situ Gellation
Various polymers are capable
of prolonging the residence time of drug delivery systems by their in-situ
gelling properties. For instance, deacetylated gellan gum is used in eye
drops (Timoptic XE; CibaVision) in order to
prolong the precorneal residence time of the incorporated drug. Such in-situ
gelling properties are also beneficial for numerous other drug delivery
systems improving the bioavailability and prolonging the drug action [Park J.S., Oh Y.K., Yoon H., Kim J.M., and Kim C.K. (2002). In situ gelling and mucoadhesive polymer vehicles for controlled intranasal delivery of plasmid DNA. J. Biomed Mater. Res.,59, 144; Bromberg, L.E. (2001) Enhanced nasal retention of hydrophobically modified polyelectrolytes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 53, 109; Paulsson M., Hagerstrom H., and Edsman K. (1999). Rheological studies of the gelation of deacetylated gellan gum (Gelrite) in physiological conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 9, 99]. In comparison
to so far used in-situ gelling polymers, thiolated polymers are capable of
providing a comparatively more pronounced increase in viscosity after
application, as an extensive crosslinking process by the formation of
disulfide bonds between the polymer chains takes place. For instance, in
case of thiolated chitosan a more than 1000-fold increase in viscosity by
the formation of disulfide bonds within the polymeric network based on a
simple oxidation process was shown [Bernkop-Schnürch, A., Hornof, M. and Zoidl, T. (2003). Thiolated polymers – thiomers: modification of chitosan with 2-iminothiolane, Int. J. Pharm., 260, 229]. Being applied in liquid form, they become highly viscous gels for instance
in the nasal cavity or in the vagina, which avoids an unintended rapid
elimination of the semisolid delivery system.
|
|
News
Thiomatrix joined the EU-project TENTACLE (101191747) focusing on the use of thiomers for in situ bioprinting.
more....
|
|
ThioMatrix Hotline:
+43 512 890046
Mo-Th 9.00-17.00
and Fr 9.00-14.00
 Print this page
Print this page
|
Download references about thiomers
|
|


